|
|
|
|
EXTRACTION
OF IRON
|
|||||
|
INTRODUCTION
|
|||||
| Iron is extracted from its oxide | ore called HAEMATITE (Fe2O3). | ||||
|
PRINCIPLE
OF EXTRACTION
|
|||||
| Extraction of iron is based on the reduction of HAEMATITE (Fe2O3) with carbon.. | |||||
|
DETAILS
OF EXTRACTION
|
|||||
| The process of the extraction of iron is carried out by the following steps: | |||||
| Concentration
of ore: In this metallurgical operation, the ore is concentrated by removing impurities like soil etc. The process involves the crushing and washing of ore. |
|||||
| Calcination
or Roasting of ore: The concentrated ore is now heated in the presence of air. The process of roasting is performed to remove moisture, CO2, impurities of sulphur, arsenic. Ferrous oxide is also oxidized to ferric oxide. |
|||||
|
Reduction
of ore
|
|||||
| The process of reduction is carried out in a blast furnace. | |||||
|
Blast
Furnace
|
|||||
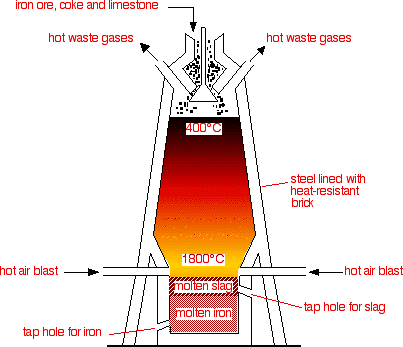
| The blast furnace is a cylindrical tower like structure about 25m to 35m high. It has an outer shell of steel. Inside of furnace is lined with fire bricks. The top of the furnace is closed by a cup-cone feeder. | |||||
|
|
|||||
|
The
charge
|
|||||
|
The charge
consists of : roasted ore Coke Limestone |
|||||
|
Details
of reduction
|
|||||
| The charge is fed into the furnace from its top. A preheated blast of air at 1500OC, is blown into the furnace under pressure near to the bottom. The blast oxidizes carbon to CO2. | |||||
|
C
+ O2
|
|||||
| Formation of CO2 is an exothermic reaction in which a huge amount of heat is liberated which rises the temperature to 1900OC in this region. As the CO2 passes upwards, it reacts more coke to form carbon monoxide. | |||||
|
CO2
+ C
|
|||||
| Formation
of CO is an endothermic reaction and the temperature in this region falls
to 1100OC. CO is the main reducing agent in the upper portion of blast furnace. |
|||||
| Reactions in blast furnace | |||||
|
Fe2O3
+ 3C
Fe3O4 + 4CO CO2 + C |
|||||
|
Overall
reaction
|
|||||
|
Fe2O3
+ 3CO
|
|||||
| The liquid iron runs downward to the bottom of the furnace and is withdrawn through tap hole. | |||||
|
Slag
formation
|
|||||
| Lime stone on heating decomposes to CaO and CO2. | |||||
|
CaCO3
|
|||||
| CaO
now reacts the impurities of ore called GANGUE to form slag. Slag is the
mixture of CaSiO3 and Ca(AlO2)2. The slag floats over the top of molten iron. Slag is a useful byproduct. It is used in road making, cement manufacturing a light weight building materials. |
|||||
|
Flux
+ Gangue
CaO + SiO2 CaO + Al2O3 |
|||||
 blust furnance blust furnance | |||||
No comments:
Post a Comment